Home » Circuits
Reverse Polarity Protector
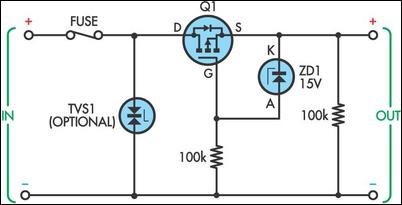
A series diode is often used as a means of protecting equipment from accidental power supply reversal, particularly in battery-powered equipment. Due to forward voltage losses, this is sometimes impractical. One solution is to use an enhancement mode P-channel power Mosfet (Q1) in series with the positive supply rail. A device with low drain-source "on" resistance can be selected to minimise voltage losses, which in turn extends battery life and reduces heat dissipation.Circuit diagram:
Zener diode ZD1 must be included to protect against excessive gate-source voltage, while a 100kΩ resistor limits zener fault current. A second 100kΩ resistor across the output ensures that the gate doesn’t float when the input is disconnected. A series fuse and bidirectional transient voltage suppressor (TVS1) could be included to provide over-voltage protection, if desired. If common input & output grounds are unimportant, then a version of this circuit employing an N-channel power Mosfet in series with the negative (0V) rail could also be employed.
Author: Bruce Griffiths - Copyright: Silicon Chip Electronics