Home » Circuits
Slave Flash Trigger
Using any camera in a dull or dark environment generally requires the use of supplementary light. This is a standard technique, and even where adequate natural lighting exists, to take conventional film pictures with enhanced contrast using a ‘fill-in’ flash for foreground subjects in shade. A flash is often built into the camera body, but the internal flash is not usually powerful enough to illuminate subjects much more that 3 m or so from the camera.On SLR cameras a hot-shoe is provided for triggering an auxiliary, more powerful flash, but the small pocket cameras are not so equipped. However, it is possible to trigger a slave flash from the camera flash by optical means. Even so, things are not so simple, for some cameras, e.g. Olympus, Nikon, Canon actually fire twice, although it appears to be once to the naked eye. The first flash sets the exposure and the second takes the picture. Help on synchronisation requirements may be found at various websites maintained by professional photographers.
Circuit diagram:
See also www.caves.org.uk/flash/docs.html for a series of articles with kits by a caving enthusiast. The presented trigger circuit optically receive the camera flashes and either fires at the same time as the first flash or has one flash delay before triggering the slave flash. Additional counting circuitry is required for more than one delay (covered by modified circuit not presented here). Here’s how it works.
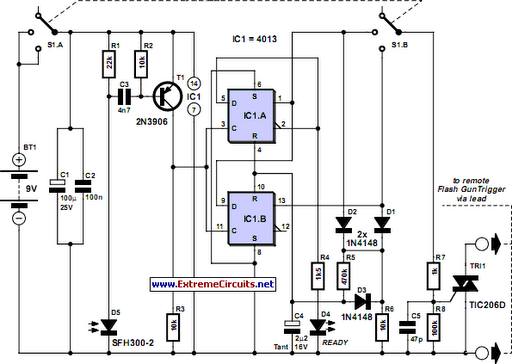
The response of phototransistor D5 to the external camera flash is pulsed by a transistorised amplifier T1 into the dual flip-flop clock IC1. One output of a flip-flop illuminates an LED as a ‘ready’ signal. A double pole 3-position slide switch, S1, selects none (e.g. for Kodak camera) or one (e.g. for Olympus camera) flash delay before triggering. Both flip-flops are used in the 4013, the clock signal derived from the flash is used (triggered on the rising clock signal) to ‘divide by two’ and trigger the TIC206 triac on the first or second flash.
A simple RC timed reset mechanism around R6-C4 is used with a relatively long delay (about half a second) before resetting the entire circuit. The advantage of the triac is that a trigger voltage of either polarity can be handled. The 2N3906 may be replaced by its near equivalent the BC212L. The SFH300-2 photodiode is supplied by Maplin as part number MES NP64U. The triac may also be a TIC126D.
Author: Peter Metcalfe
Copyright: Elektor Electronics
Copyright: Elektor Electronics