Home » Circuits
High-Current Battery Discharger
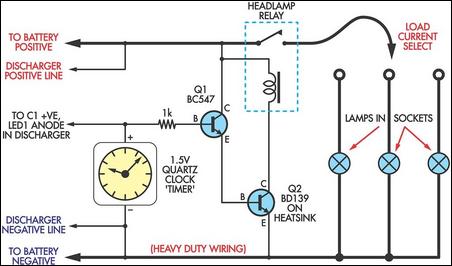
If you have a motley collection of 12V batteries in varying states of health, this simple circuit will allow you to easily check their capacity. It's basically a high-current discharge load which is controlled by the NiCd Discharger. This involved increasing the existing 10µF capacitor across LED1 to 100µF, to enable it to supply the brief current pulses required by the clock mechanism. The discharger's "clock connection" now controls a BC457/BD139 Darlington transistor pair (Q1 & Q2) via a 1kO resistor. These in turn activate a car headlamp relay to switch in a preselected lamp load (one of three).Circuit diagram:
With 12V selected, the prototype unit stops the discharge at 11.4V which corresponds to a cell voltage of 1.9V (this is a pretty good indication of a discharged 12V battery). The loads consist of three automotive lamps, selected to provide discharge rates to suit the battery being tested. These lamps should be fitted to sockets, so that they can be easily swapped for other lamps with different wattages, if required. That way, the discharge current can be varied simply by changing the lamp wattage. By the way, this circuit will also work with 6V batteries, provided the relay holds in. This gives an "end-point" voltage of about 5.7-5.8V.
Author: Reg Carter - Copyright: Silicon Chip Electronics