Home » Circuits
Infra-Red Level Detector
Useful for liquids level detection and proximity devices, Up to 50 cm. range, optional relay operationThis circuit is useful in liquids level or proximity detection. It operates detecting the distance from the target by reflection of an infra-red beam. It can safely detect the level of a liquid in a tank without any contact with the liquid itself. The device's range can be set from a couple of cm. to about 50 cm. by means of a trimmer. Range can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and is mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device's sensitivity.
Circuit diagram:
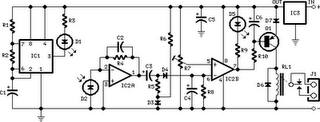 Parts:
Parts:R1_____________10K 1/4W Resistor
R2,R5,R6,R9_____1K 1/4W Resistors
R3_____________33R 1/4W Resistor
R4,R8___________1M 1/4W Resistors
R7_____________10K Trimmer Cermet
R10____________22K 1/4W Resistor
C1,C4___________1µF 63V Electrolytic or Polyester Capacitors
C2_____________47pF 63V Ceramic Capacitor
C3,C5,C6______100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors
D1_____________Infra-red LED
D2_____________Infra-red Photo Diode (see Notes)
D3,D4________1N4148 75V 150mA Diode
D5______________LED (Any color and size)
D6,D7________1N4002 100V 1A Diodes
Q1____________BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistor
IC1_____________555 Timer IC
IC2___________LM358 Low Power Dual Op-amp
IC3____________7812 12V 1A Positive voltage regulator IC
RL1____________Relay with SPDT 2A @ 220V switch Coil Voltage 12V. Coil resistance 200-300 Ohm
J1_____________Two ways output socket
Circuit operation:
IC1 forms an oscillator driving the infra-red LED by means of 0.8mSec. pulses at 120Hz frequency and about 300mA peak current. D1 & D2 are placed facing the target on the same line, a couple of centimeters apart, on a short breadboard strip. D2 picks-up the infra-red beam generated by D1 and reflected by the surface placed in front of it. The signal is amplified by IC2A and peak detected by D4 & C4. Diode D3, with R5 & R6, compensates for the forward diode drop of D4. A DC voltage proportional to the distance of the reflecting object and D1 & D2 feeds the inverting input of the voltage comparator IC2B. This comparator switches on and off the LED and the optional relay via Q1, comparing its input voltage to the reference voltage at its non-inverting input set by the Trimmer R7.
Notes:
- Power supply must be regulated (hence the use of IC3) for precise reference voltage. The circuit can be fed by a commercial wall plug-in adapter, having a DC output voltage in the range 12-24V.
- Current drawing: LED off 40mA; LED and Relay on 70mA @ 12V DC supply.
- R10, C6, Q1, D6, D7, RL1 and J1 can be omitted if relay operation is not required.
- The infra-red Photo Diode D2, should be of the type incorporating an optical sunlight filter: these components appear in black plastic cases. Some of them resemble TO92 transistors: in this case, please note that the sensitive surface is the curved, not the flat one.
- Avoid sun or artificial light hitting directly D1 & D2.
- Usually D1-D2 optimum distance lies in the range 1.5-3 cm.
